- Private & confidential service
- Genuine medication
- All-inclusive service - No hidden fees
- Next day delivery
- Weight Loss
- A guide to prescription weight loss treatments
- Wegovy interactions: what you need to know
Wegovy interactions: what you need to know
Wegovy is a weight loss medication that works by reducing your appetite. It can be highly effective, especially for those who struggle to lose weight through diet and exercise alone.
However, it is still a prescription medicine. So, it can have interactions with other medications you take. If you’re considering Wegovy injections and you take other medications, keep reading to learn more about Wegovy interactions.
Why is it important?
When you start a new medication, it’s important to know all the potential undesirable effects and interactions with your current meds.
One medication can alter the effects of another. It could increase the effects of one medication, increasing the risk of side effects. Alternatively, it could decrease the effects of another medicine. This could mean it isn’t effectively managing the condition it is meant to treat.

Always tell your healthcare provider what medications you take and what they are for. This will prevent any risk of adverse effects.
What medicines interact with Wegovy (Semaglutide)?
Wegovy and other medications containing Semagutide work by reducing your appetite. It increases the production of certain hormones that affect your hunger, meaning you eat less over time.
However, this can affect your digestion and metabolism in different ways. This can affect certain medicines. Below are some of the most common interactions
| Type | Medicine(s) | Interaction with Wegovy |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes medicines | Insulin | Can increase the risk of significantly low blood sugar levels (hypoglycaemia). |
| Sulphonylureas (e.g. gliclazide and glimepiride) | ||
| DPP-4 inhibitors (e.g. sitagliptin and linagliptin) | ||
| Metformin | ||
| Repaglinide | ||
| Acarbose | ||
| Thyroid medicines | Levothyroxine | Can increase the effects of Levothyroxine and alter your thyroid function. |
| Anti-epileptics | Fenfluramine | Can increase the risk of significantly low blood sugar levels (hypoglycaemia). |
| Oral contraceptives | The combined pill | Wegovy can cause sickness/diarrhoea as a side effect, which can reduce the effectiveness of contraception. |
| The progestogen-only pill (mini-pill) | ||
| The morning-after pill |
Diabetes medicines
The most common Wegovy interaction is with diabetes medicines. It can interact with the following:
- insulin
- sulphonylureas (e.g. gliclazide and glimepiride)
- DPP-4 inhibitors (e.g. sitagliptin and linagliptin)
- metformin
- repaglinide
- acarbose
One of the ways Wegovy works is by reducing your blood sugar, which is why it was originally licensed for treating type 2 diabetes.
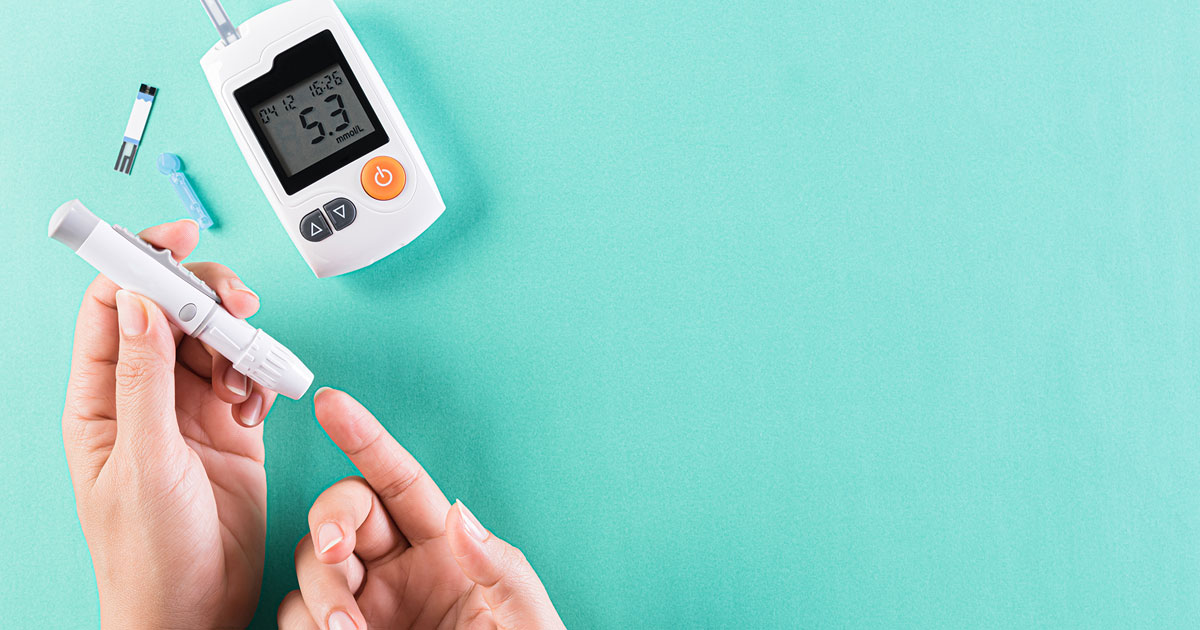

When taken with another diabetes medicine, it can cause dangerously low blood sugar levels. This is a condition known as hypoglycaemia or ‘hypo’. This can cause symptoms such as dizziness, sweating, confusion and weakness. A full list of hypo symptoms can be found in the Wegovy patient information leaflet.
It may also increase your risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. This is a serious condition where a lack of insulin causes ketones to build up in the blood. It is more common in type 1 diabetes but can happen to people with type 2. It causes extreme thirst, stomach pain, fruity-smelling breath and other symptoms. It requires urgent treatment so do not ignore any symptoms.
You can take Wegovy or Semaglutide with your regular diabetes medication. However, your doctor will want to alter the dose or change your treatment plan to reduce the risk of an interaction.
Thyroid medicines
Levothyroxine is a medication prescribed to those with hypothyroidism, otherwise known as an underactive thyroid.
Studies show that Semaglutide can increase the effect of Levothyroxine. This could alter your thyroid function.
If you take Levothyroxine, you should talk to your doctor before starting Wegovy. They may need to alter your dose or suggest an alternative to Wegovy.
Anti-epileptics
Fenfluramine is a medication used to manage and prevent seizures. Some research has found that it can reduce blood sugar levels. So, like with diabetes medicines, it could increase your risk of ‘hypo’.
If you take an antiepileptic, check with your doctor before using Wegovy or Semaglutide so they can check it’s safe to use.
Oral contraceptives
While not a direct interaction, Wegovy can cause side effects that may affect oral contraception. This includes the combined pill, the mini-pill and the morning-after pill.
Common side effects of Wegovy can include vomiting or diarrhoea. Both can affect the absorption of the pill into your body and make it less effective.
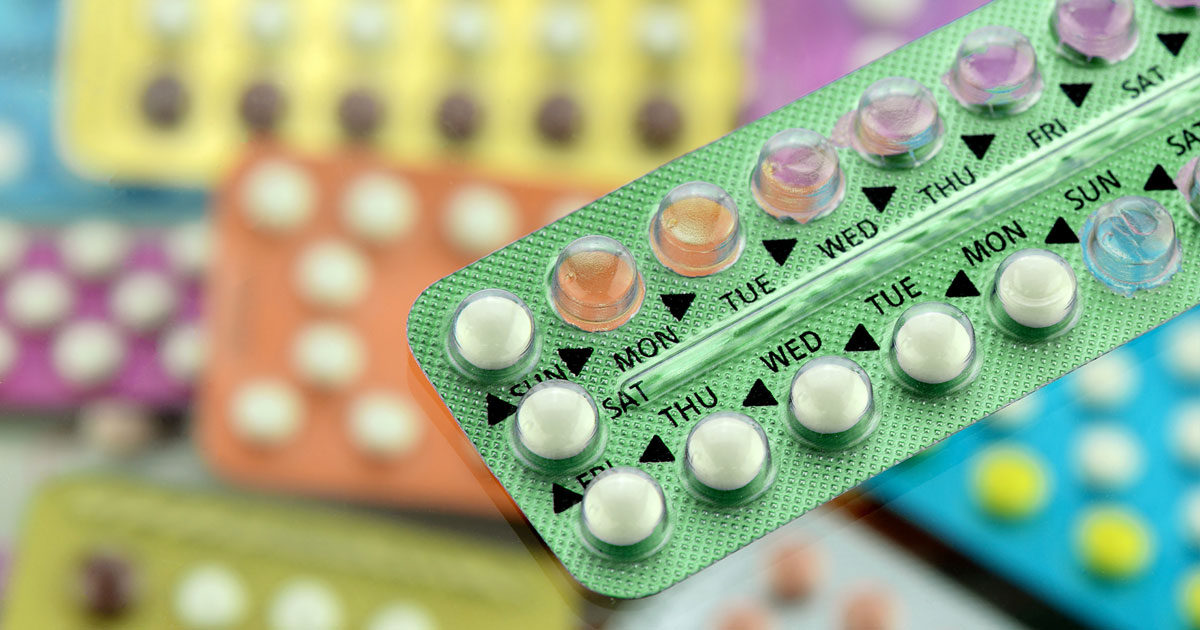
If you vomit within 3 hours of taking the combined pill or within 2 hours of taking the mini-pill or morning-after pill, your contraception may be affected. Regarding diarrhoea, 6-8 loose bowel movements within 24 hours may also affect contraception absorption.
If you experience these side effects on Wegovy, you should use barrier contraception or abstain from sex while you’re sick and for 2 days after you have recovered. If you have had unprotected sex in that time, you should take a pregnancy test.
Do food or drinks react with Wegovy?
Some medications must be taken on an empty stomach or with food. Luckily, in the case of Wegovy, you don’t have to worry. You can take it any time of the day regardless of meals. This is not true of all weight loss medications, however, so always refer to the patient information leaflet.
In addition, foods and drinks are known for altering the effects of some medications. This includes grapefruits, grapefruit juice, leafy green vegetables and foods high in potassium like bananas.

None of these foods affect how Wegovy works. However, you may want to reduce caffeine and spicy foods. They can speed up digestion which could increase your risk of side effects like diarrhoea or heartburn.
You will also need to alter your diet overall to lose weight on Wegovy. You should stick to a low-calorie diet and make healthy food choices. Alongside increased physical activity, a healthy diet will increase weight loss on Wegovy.
Alcohol and Wegovy
You should also limit your alcohol intake. Drinking alcohol on Wegovy can also increase your risk of developing pancreatitis, a condition that causes inflammation of the pancreas. This condition can be fatal and requires immediate treatment.
Alcoholic drinks also can contain a lot of calories, which can impact your weight loss efforts. It may also worsen any side effects like nausea if you experience them.
Can I take herbal medicines with Wegovy?
Herbal remedies contain active ingredients from plants and are considered a natural way to treat some conditions that can be self-medicated (e.g. coughs and colds).
One significant risk of taking herbal medicines is that they can affect any medicines you currently take. Well-known examples include St John’s wort, Gingko Biloba and Ginseng.
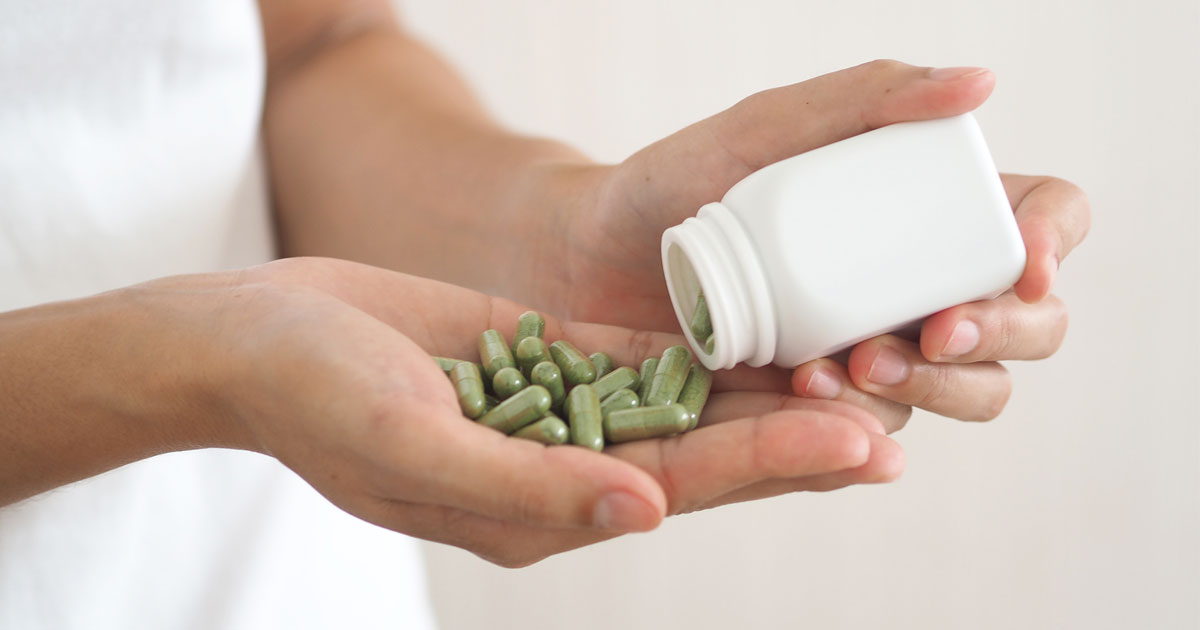

There are no known notable interactions between Wegovy and herbal medicines. However, you should always ask a healthcare professional before starting any herbal remedy.
Can I take Wegovy with other medicines?
If you’re interested in taking Wegovy but take any other medications or have a pre existing medical condition, you must speak to your doctor beforehand.
If you take one of the medications we listed, your doctor may be able to adjust your dose or change your treatment plan to accommodate you taking Wegovy.
There are also several prescription weight loss alternatives available, such as Saxenda, Orlistat and Mysimba. Read the patient leaflet and ask your doctor to make sure weight loss treatment is suitable for you.
If you choose HealthExpress as your Wegovy provider, we complete a comprehensive medical review to ensure that it is safe for you to take. So, it’s important that you’re honest about your medical history. If our doctors don’t think Wegovy is right for you, then they will suggest a safe alternative.
Further reading

A guide to prescription weight loss treatments 5 ways to increase weight loss on Wegovy
Reviewed by Dr. Plauto Filho
A guide to prescription weight loss treatments Ozempic weekly injection pen
Reviewed by Dr. Plauto Filho
A guide to prescription weight loss treatments Side effects of Liraglutide and how to manage them
Reviewed by Dr. Plauto Filho
A guide to prescription weight loss treatments Semaglutide: what to expect and when
Reviewed by Dr. Plauto Filho
A guide to prescription weight loss treatments Semaglutide side effects: what you need to know
Reviewed by Dr. Plauto Filho
A guide to prescription weight loss treatments What semaglutide dose should I take?
Reviewed by Dr. Plauto Filho
A guide to prescription weight loss treatments An introduction to GLP-1 agonists for weight loss
Reviewed by Dr. Plauto Filho
A guide to prescription weight loss treatments How do I administer injections for weight loss?
Reviewed by Dr. Caroline Fontanamedical form
medication
prescription
from pharmacy

